In India, one in 10 adults has a thyroid disorder, and one in 11 lives with diabetes. Surprisingly, about 1 in 4 people with Type 2 diabetes also have hypothyroidism. This is no coincidence—both conditions affect how the body uses energy.
Thyroid hormones and insulin work together to manage energy and blood sugar. When one is out of balance, it often disrupts the other.
What is the Thyroid?
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Despite its small size, it plays a powerful role in regulating various bodily functions.
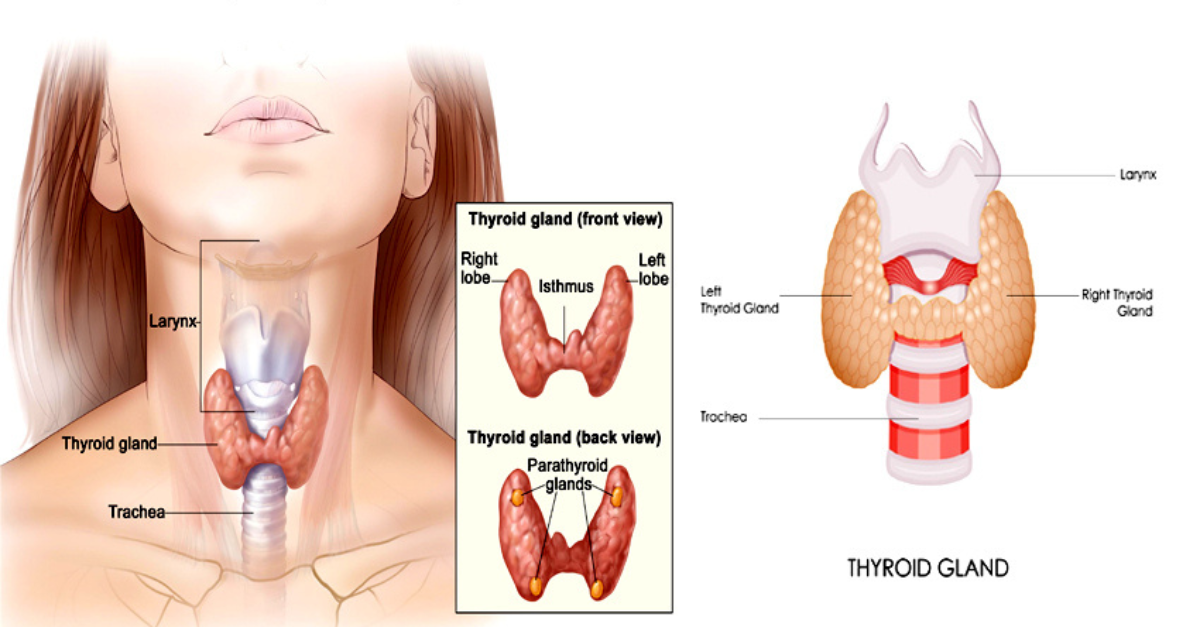
Functions of the thyroid gland
- Regulates metabolism
- Controls heart rate
- Maintains body temperature
- Supports brain development and mood
- Influences energy levels
The thyroid produces hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are regulated by the pituitary gland via thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition where the body fails to regulate blood sugar (glucose) properly.
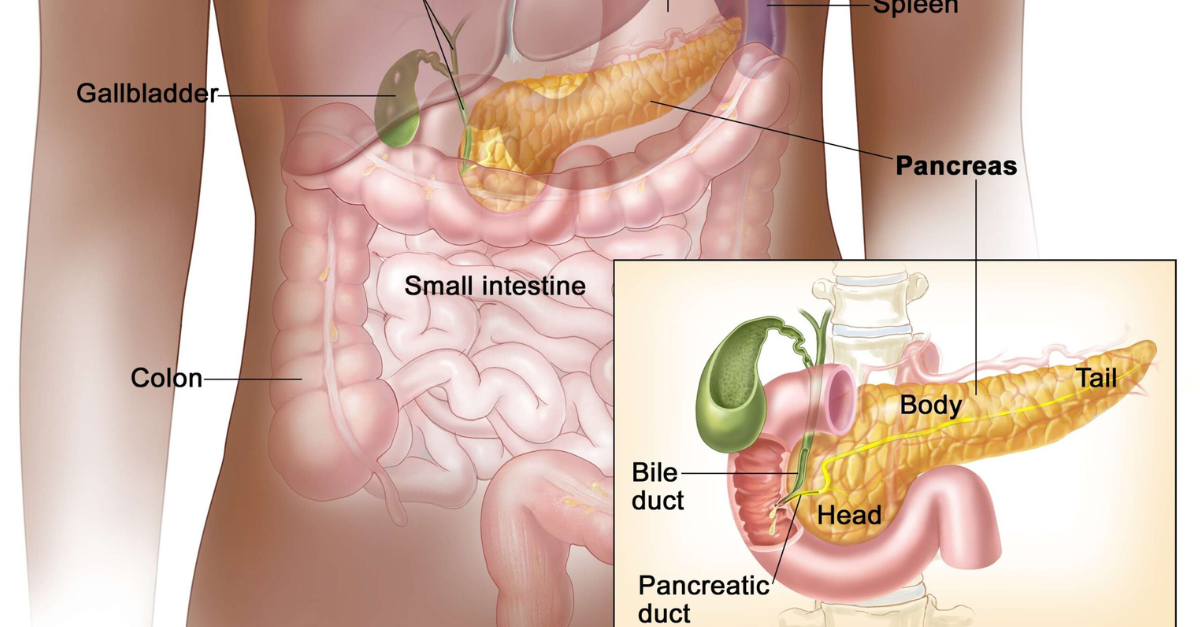
Insulin, the hormone produced by the pancreas, allows glucose to enter cells for energy. In diabetes, this process is impaired, leads to high blood sugar levels.
It is broadly classified into:
A. Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
B. Type 2 Diabetes
A metabolic disorder resulting in insulin resistance and reduced insulin production over time. It’s more common and often linked to obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetics.
C. Gestational Diabetes
Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after delivery but increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes later in life.
How Are Thyroid and Diabetes Connected?
The thyroid and pancreas are both part of the endocrine system, which controls hormone release throughout the body. When one part of this system is compromised, it often affects other areas.
1. Autoimmune in Origin
People with Type 1 diabetes are at higher risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disorders, especially Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (hypothyroidism) and Graves’ disease (hyperthyroidism).
Both diseases may have genetic links involving autoimmune susceptibility genes such as HLA-DR and CTLA-4.
2. Impact on Blood Sugar Control
Hypothyroidism can slow down glucose metabolism, leading to increased insulin sensitivity. This may cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) in diabetic patients.
Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, increases insulin resistance and liver glucose production, leading to hyperglycemia.
3. Metabolic Interference
Thyroid hormones influence:
Insulin secretion
Carbohydrate metabolism
Cholesterol levels
Weight gain/loss
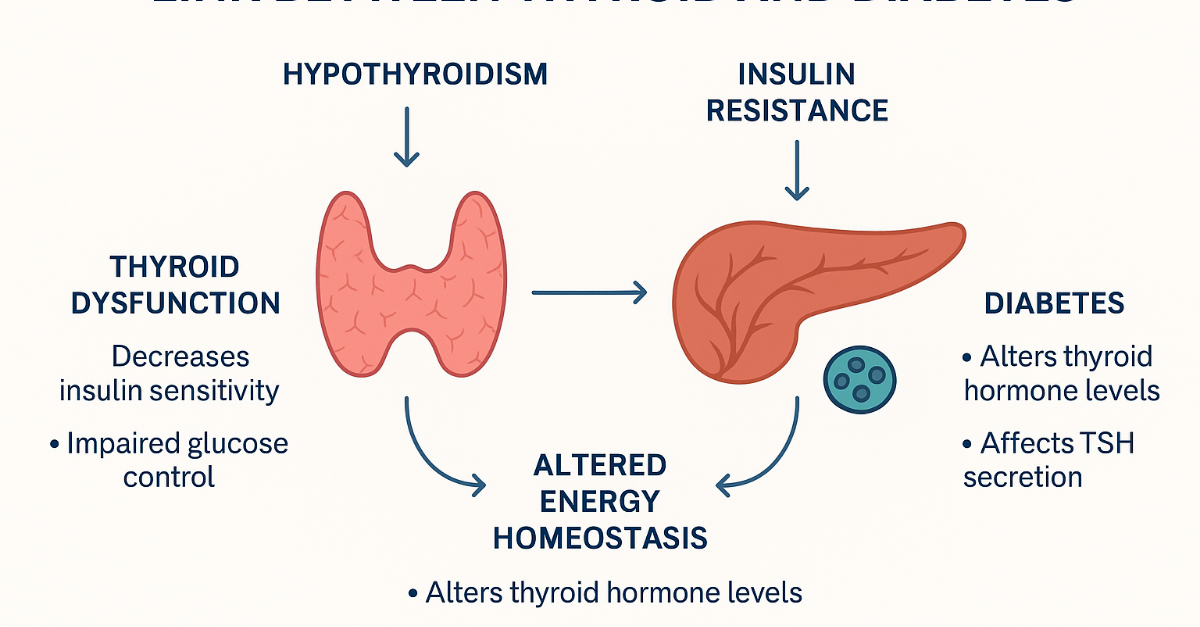
Disease Cycle (Patho-Physiology)
Below is the diagram showing ” Thyroid and Its Connection With Diabetes ”