The Science Behind the Stages of Human Sleep
Sleep is one of the most important functions of the human body. It helps our brain recharge, our body repair, and our energy restore for the next day.

Yet, sleep is not just about closing your eyes and waking up hours later.
During the night, the human body goes through different stages of sleep—each with a unique role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
we will break down the stages of human sleep explained simply so you can understand what happens to your body and mind when you rest.
Read more @: Science of sleep
Why Understanding Sleep Stages Matters
Before diving into the stages, it’s important to understand why sleep cycles are so crucial. When you don’t get enough quality sleep or your stages of sleep are interrupted, you may experience:
- Daytime fatigue and lack of focus
- Poor memory and reduced cognitive function
- Weakened immune system
- Increased risk of health issues like obesity, heart disease, and diabetes
By learning about sleep stages, you’ll better understand why quality sleep is just as important as quantity.
The Two Main Types of Sleep
Sleep is divided into two main categories:
1. Non-REM Sleep (Non-Rapid Eye Movement)
2. REM Sleep (Rapid Eye Movement)
Non-REM sleep itself has three stages, while REM sleep stands as its own stage. Together, they make up a complete sleep cycle.
A full sleep cycle usually lasts 90 to 110 minutes, and during a typical night, you go through four to six sleep cycles.
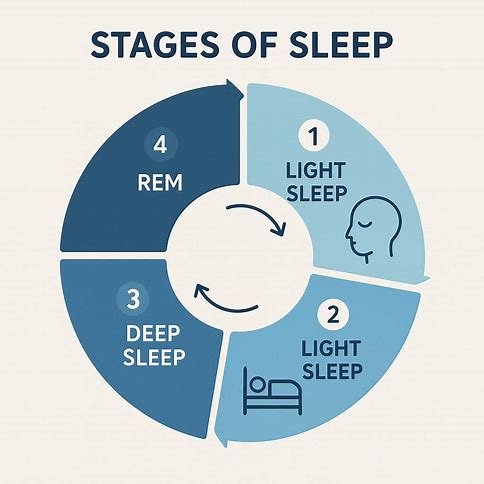
Stage 1: Light Sleep (Non-REM)
This is the first stage of sleep and marks the transition from being awake to drifting into sleep. It usually lasts only a few minutes.
What happens in Stage 1?
- Your muscles relax.
- Breathing becomes slower.
- Brain waves start to slow down.
- It’s easy to wake up during this stage.
Stage 1 acts as a gateway into deeper sleep. If you’ve ever felt yourself “jerk awake” just as you were dozing off, that’s because of sudden muscle contractions often happening in this stage.
Stage 2: Deeper Light Sleep (Non-REM)
Stage 2 is where your body starts to settle in for real rest. It is considered light sleep, but you are more detached from the external environment compared to Stage 1.
What happens in Stage 2
- Heart rate and breathing become even steadier.
- Body temperature drops.
- Brain activity slows, but short bursts of activity (called sleep spindles) appear.
Stage 2 makes up the largest portion of human sleep—almost 50% of the total night. It plays a key role in memory consolidation and learning.
Stage 3: Deep Sleep (Non-REM)
This is often called slow-wave sleep or deep sleep, and it is the most restorative stage.
What happens in Stage 3?
- Brain waves are at their slowest.
- Blood pressure drops and muscles fully relax.
- Tissue growth and repair take place.
- The body releases growth hormones.
Deep sleep is the time when the body heals, builds muscle, and strengthens the immune system. If you wake up from this stage, you may feel groggy and disoriented. This is known as sleep inertia.
Stage 4: REM Sleep (Rapid Eye Movement)
After deep sleep, your body moves into REM sleep, the stage most famous for dreaming. It usually starts about 90 minutes after falling asleep and becomes longer with each cycle throughout the night.
What happens in REM sleep?
- Eyes move rapidly under closed eyelids.
- Brain activity increases, similar to when you’re awake.
- Heart rate and blood pressure rise.
- Most vivid dreams occur.
Body experiences temporary paralysis to prevent acting out dreams.
REM sleep is critical for emotional regulation, creativity, and memory processing. It’s also when your brain clears out unnecessary information and strengthens useful connections.
The Full Sleep Cycle in Action
To put it all together, here’s how a normal sleep cycle looks:
- 1. Stage 1 (light sleep) – a few minutes
- 2. Stage 2 (light but deeper sleep) – about 20 minutes
- 3. Stage 3 (deep sleep) – longer in the first half of the night
- 4. REM sleep – longer in the second half of the night
As the night progresses, your body spends less time in deep sleep and more time in REM sleep. That’s why getting a full night’s rest is essential. Cutting sleep short means you miss out on those longer REM periods.
Why Each Stage of Sleep Is Important
Each stage of human sleep has its unique role in maintaining health:
Stage 1 & 2 (Light Sleep): Help your body relax, regulate heartbeat and temperature, and prepare for deeper stages.
Stage 3 (Deep Sleep): Crucial for physical recovery, cell repair, and immune function.
Stage 4 (REM Sleep): Vital for memory, learning, emotional balance, and creativity.
Skipping or disrupting any stage can impact your body and mind.
For example, not enough deep sleep can leave you physically exhausted, while lack of REM sleep can affect your mood and memory.
Factors That Can Disrupt Sleep Stages
Unfortunately, many factors interfere with natural sleep cycles, such as:
- Stress and anxiety – keeping the brain active at night.
- Caffeine or alcohol – disturbing REM and deep sleep.
- Irregular sleep schedule – confusing the body’s internal clock.
- Medical conditions – like sleep apnea, which interrupts breathing and rest.
- Excessive screen time – blue light delays melatonin release.
By managing these factors, you can improve the quality of each sleep stage.
Tips for Better Sleep Cycles
To make sure you go through all the stages of sleep effectively, try these sleep hygiene tips:
1. Stick to a schedule – go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
2. Create a bedtime routine – such as reading, meditation, or light stretching.
3. Limit caffeine and alcohol – especially in the evening.
4. Reduce screen exposure – at least one hour before bedtime.
5. Keep your sleep environment cool, dark, and quiet.
6. Exercise regularly, but not too close to bedtime.
7. Avoid heavy meals late at night.
These practices help you move smoothly through all stages of human sleep, ensuring restorative rest.
Final Thoughts
Sleep is not a single state but a complex process made up of different stages. From light sleep to deep sleep and REM, each stage has a vital role in repairing the body, sharpening the mind, and balancing emotions.
When you understand what happens during the stages of human sleep, you can take steps to improve your sleep quality and, in turn, your overall health.
So, the next time you wake up feeling refreshed after a full night’s rest, remember—it’s because your body successfully moved through the amazing stages of human sleep.